WATCH: Report says national student debt is over $1.6 trillion
The college student loan balance in the United States is $1.66 trillion, according to a WalletHub report.
To determine the best and worst states with student debt, the WalletHub’s report compared all 50 states and the District of Columbia. WalletHub also graded on a 100-point scale focusing on metrics such as the state’s cost of living, unemployment rates and paid internship opportunities for students.
The state with the most student debt is Mississippi.
The average amount of student loans owed, according to the report, equals 56% of the median income in the state. Mississippi residents hold a total of $17 billion in student loan debt.
Additionally, Mississippi has the 14th-highest default rate of debt, meaning people are having trouble paying the loans they borrow, the report stated.
The report indicates Mississippi has the fourth-worst availability of jobs to students, and the second-lowest share of paid internships, behind Louisiana.
“In a state like Mississippi, they may not have the highest balance, student loan balance per resident, but because it’s such a low-income state, the economy is in pretty poor shape right now, so they’re devoting more of their income towards student loan debt,” WalletHub Analyst Chip Lupo told The Center Square. “Now juxtapose that with a state like, say, California at 49. They have the highest student loan debt, the highest amount of debt, but because it’s a pretty high-income state, residents aren’t allocating as much of their income towards the debt.”
In California, $151.5 billion in student debt is owed by state residents. At the same time, the state has a multitude of grant and loan forgiveness programs.
Following Mississippi, states with the most student debt, with the average amount owed per student, are New Hampshire, $34,860; Pennsylvania, $36,120; Delaware, $38,856, and South Dakota, $31,171.
The states with the least amount of student debt are Washington, with the average student owing $36,709; New Mexico, $34,246; California, $38,300; Utah, $33,872; and Hawaii, with $38,929.
Lupo said the rise in student debt has been a cause of the rise in the cost of tuition, which has doubled in the past two decades.
“I do think that in a lot of states if we shift more of the student loan programs back to the banks, create some more competition, I do think that college would be a little bit more affordable, and students would have a little bit more leeway and maybe not have to borrow as much,” Lupo said.
In recent years, the student loan forgiveness program, strongly advocated by the Biden administration, provided relief for over 5 million borrowers, upward of $190 billion. That is only 11% of the current national student loan debt relieved.
“I think there were all kinds of legal issues involved with the Biden administration’s effort to forgive student loans,” Lupo said. “You can’t erase the debt.”
Latest News Stories

Executive Committee Considers $12,000 Strategic Planning Initiative with University of St. Francis

Illinois takes over health insurance marketplace in 2026 amid skepticism

WATCH: IL state reps challenge IEMA-OHS responses to local agencies

Judge expands restraining order against ‘Beto’ O’Rourke, adds ActBlue

Reversing Biden’s precedent, students complete FAFSA in minutes at beta-testing event

Trump, Zelenskyy to meet Monday in steps toward peace with Russia

Executive Committee Members Decry Roadside Litter, Call for Action Against Garbage Haulers

Possible ‘agreement’ reached in Trump-Putin meeting; more discussion likely

WATCH: Gun rights supporters celebrate 9th Circuit’s ruling against CA gun rationing law

Feds sue California over emission standards for trucks
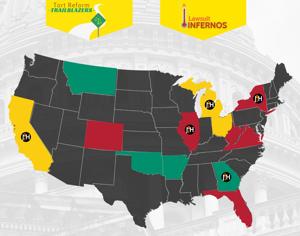
Illinois quick hits: ‘Lawsuit inferno’ bill takes effect after Pritzker signed 267 measures Friday
WATCH: UW-authored study on surgery times contradicts CMS basis for reimbursement cuts